The world of artificial intelligence (AI) is vast and ever-evolving. In just a few years, we have moved from automation to RPA to ChatGPT and GenerativeAI. One groundbreaking advancement in this domain is Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). For those unfamiliar, this technology might sound complex. However, with a brief dive, you’ll find that GANs offer an exciting glimpse into the future of AI. For a greater deep dive, check out our next blog on NLPs and GANs.
A Basic Overview of GANs
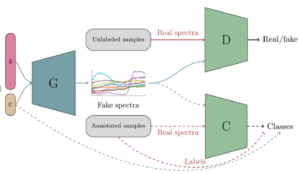
Firstly, let’s break down the term. Generative Adversarial Networks consist of two parts: the “generator” and the “discriminator.” The generator creates images, while the discriminator evaluates them. Consequently, these two parts work in tandem, constantly learning and refining their processes. As a result, the generated images become increasingly sophisticated.
How Do GANs Function?
Now, you might wonder how these networks function. At the start, the generator creates a random image. Subsequently, the discriminator assesses this image against real ones. After that, it provides feedback. Based on this feedback, the generator then makes adjustments. Therefore, with each cycle, the artificial images become more realistic.
Applications of Generative Adversarial Networks
Furthermore, the practical applications of GANs are varied and expansive. For instance, artists and designers use GANs to create unique artwork. Similarly, the film industry leverages these networks for special effects. Also, in the medical field, researchers employ GANs to simulate cellular structures for study.
Challenges and Controversies
However, as with many innovative technologies, GANs come with challenges. For one, the training process can be unstable. There are times when the generator creates unrealistic images, and the discriminator can’t provide accurate feedback. Moreover, there are ethical concerns too. For example, deepfake videos, which can manipulate real footage, are created using Generative Adversarial Networks. Consequently, these videos can spread misinformation or be used for malicious purposes.
Future Prospects and Potential
On the other hand, the potential of GANs is immense. In the coming years, experts predict that we’ll see even more refined applications. For example, virtual reality environments could become more realistic with the help of GANs. Additionally, industries like fashion and architecture might utilize these networks for design prototypes. In essence, the possibilities are vast.
Conclusion
Generative Adversarial Networks represent a significant leap in AI technology. Despite their challenges, their potential to revolutionize industries is undeniable. Furthermore, as we continue to refine and understand GANs better, it’s exciting to ponder the myriad ways they might shape our future. As always, with great power comes great responsibility. Therefore, while we harness the capabilities of GANs, it’s essential to remain vigilant and ethical in their application.